##什么是爬山法
爬山法是局部搜索里的一种算法。爬山法就是很形象的一种算法,就像我们爬山一样,我们从山脚出发,向着山顶前进。
最陡爬山法就是我们总是向最高的地方走。例如我现在在山腰,我面前出现了3条路通向高处的路,按照我的猜想,最陡峭的一条路应该通向最高的山顶,于是我毅然决然的走向那条路。
从实际生活上推敲,我就很容易知道这个方法不是完备的,我们很可能登上一个小山坡就找不到有更高的路了。
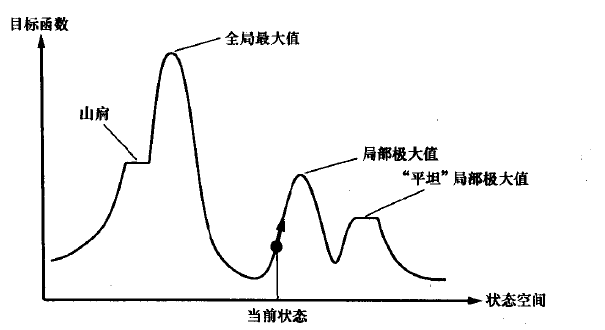
从图上可以看出,爬山法很大的几率能得出一些局部最优解,以及一些山肩,高原上的解。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Pseudocode:
function hillclimbing(problem) return a state
local variables: current, a node
neighbor, a node
current <- MAKENODE(INITIAL-STATE(problem))
While true
//如果有几个后继都是最高,那么随机选择一个
neighbor <- the highest value successor of current
//如果没有比现在更高的点,那么现在已经是所处山峰了
if(VALUE(neighbor) <= VALUE(current)) then return the STATE(current)
current <- neighbor
End While
最陡爬山法的一个问题就是,在山腰,我们面前的3条路,可能不是最陡的那一条才是通向最高峰的,而且我们面前可能有成千上万条路,我们应该更关注爬山而不是清点所有上山的路,首选爬山法为了解决这个问题,他决定从可以选择的路里随机挑一条路,只要比我现在站着的地方高,我就直接开始爬。这种方法与最陡爬山法相比,最大的好处就在于他不用找出所有的后继然后再从里面挑出一个最大值,这种方法在后继数目很多的时候会比最陡爬山法更效率一些。
1
代码只需把最陡爬山法中选节点的规则改成首选爬山法的选择规则即可。
随机重新开始爬山法解决了最陡爬山法和首选爬山法的不完备性!好了,别太兴奋,从这个算法的名字我们已经能察觉出他所谓的完备性是建立在多次的尝试上的。实际上,随机重新开始爬山法只是最陡爬山法的无限循环。当最陡爬山法没找出解,没关系,从别的山脚再爬一次嘛,多次重新爬山总能爬到全局的最高峰的嘛!在爬山法的成功率可观的时候,随机重新开始爬山法还是足够效率的,可是如果面对一些爬山法只有1%的成功率的问题的时候,随机重新开始爬山可能就极其耗费时间了。
1
代码只需在最陡爬山法返回的不是最优解的时候再次执行最陡爬山即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
/*fin 11.11
最陡爬山法
*/
#ifndef STEEPESTASCENT
#define STEEPESTASCENT
#include"queenCreator.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
bool steepest(queen q, int* sum){
q.correct();
while (true){
//根据评价函数来判断是不是到达目标状态(全局最优)
if (q.getconflict() == 0){
return true;
}
//生成后继
vector<queen> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++){
queen newq(q);
int col = i;
int row = j;
if (row == q.getrow(i)){ continue; }
newq.queenset(i, col, row);
newq.correct();
if (newq.getconflict() < q.getconflict()){
v.push_back(newq);
}
}
}
//如果没有后继比现在更高,证明已经到达的是局部最优
if (v.empty()){
return false;
}
//找出后继里最高的
int min = v[0].getconflict();
for (int i = 1; i < v.size(); i++){
if (v[i].getconflict() <= min){
min = v[i].getconflict();
}
}
vector<queen> choice;
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++){
if (v[i].getconflict() == min){
choice.push_back(v[i]);
}
}
//如果最高的有几个,那么随机选一个
int random = rand() % (choice.size());
(*sum)++;
//current <-- successor
queen q = choice[random];
q.correct();
}
}
#endif
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
/*fin 11.11
首选爬山法
*/
#ifndef FIRSTCHOICE
#define FIRSTCHOICE
#include"queenCreator.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
bool firstchoice(queen q,int* sum){
q.correct();
//int shift = 0;
while (true){
if (q.getconflict() == 0){
return true;
}
//用于记录已经扩展过的后继
int gone[8][8];
//记录扩展了几个后继
int times = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++){
gone[i][j] = 0;
}
}
int flag = 0;
while (true){
//随机生成一个后继
int col = rand() % 8;
int row = rand() % 8;
//已经扩展过所有的后继了
if (times == 56){ break; }
//已经扩展过的后继
if (gone[row][col] == 1){ continue; }
if (row == q.getrow(col)){ continue; }
queen newq(q);
newq.queenset(col, col, row);
newq.correct();
gone[row][col] = 1;
times++;
if (newq.getconflict() < q.getconflict()){
flag = 1;
q = newq;
break;
}
}
if (flag == 0){
return false;
}
(*sum)++;
}
}
#endif
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
/*fin 11.8
随机重新开始爬山法
*/
#ifndef RANDOMRESTART
#define RANDOMRESTART
#include"queenCreator.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#include"steepestascent.h"
using namespace std;
queen createnewqueen(){
queen q;
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++){
int col = j;
int row = rand() % 8;
q.queenset(j, col, row);
}
return q;
}
bool randomrestart(queen q,int* sum){
bool flag = false;
while (flag == false){
queen newq = createnewqueen();
flag = steepest(newq,sum);
}
return true;
}
#endif
1
FIN 11.11/11.41