1150-1151 1515 1007 1036 1006 1009 1050 1443 1156 1024 1063
Soj-1150 1151
 对于给定的状态,判断在规定的步数能否通过3种操作到达,输出的是步数以及操作码
对于给定的状态,判断在规定的步数能否通过3种操作到达,输出的是步数以及操作码
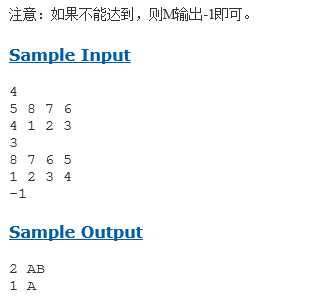
使用广度优先搜索的方法,但是考虑到广搜可以会超时以及出现重复的状态,因此广搜的过程中要实行剪枝,把已经到达过的状态剪去。 值得注意的一点是,如果使用字符串来记录上下状态,一般会超时。
因为这题有写解题报告的作业,所以直接把写了注释的代码搬过来了
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<map>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
struct magicboard{
int x;//魔板上面4个数
int y;//魔板下面4个数
string step;//到达该状态的操作串
//传入2个字符串,初始化一个魔板的状态
magicboard(string xx, string yy){
x = (xx[0] - '0') * 1000 + (xx[2] - '0') * 100 + (xx[4] - '0') * 10 + (xx[6] - '0');
y = (yy[0] - '0') * 1000 + (yy[2] - '0') * 100 + (yy[4] - '0') * 10 + (yy[6] - '0');
step = "";
}
//对魔板进行操作A,上下互换
void opA(){
int tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
step += 'A';
}
//对魔板进行操作B,向右进行循环移位
void opB(){
int x1 = (x % 10)*1000;
int x2 = x / 10;
x = x1 + x2;
int y1 = (y % 10)*1000;
int y2 = y / 10;
y = y1 + y2;
step += 'B';
}
//对魔板进行操作C,中间4个数进行顺时针旋转
void opC(){
int x1 = x / 1000;
int x2 = x / 100 - x1*10;
int x3 = x / 10 - x1*100 - x2*10;
int x4 = x % 10;
int y1 = y / 1000;
int y2 = y / 100 - y1 * 10;
int y3 = y / 10 - y1 * 100 - y2 * 10;
int y4 = y % 10;
x = x1 * 1000 + y2 * 100 + x2 * 10 + x4;
y = y1 * 1000 + y3 * 100 + x3 * 10 + y4;
step += 'C';
}
//返回步数
int stepValue(){
return step.length();
}
//重写==用于判断状态是否相同
bool operator==(magicboard e)const{
if (x == e.x&&y == e.y){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
};
int main(){
int n;
string ex;
string ey;
while (cin >> n, n != -1){
char c;
scanf("%c", &c);//接收掉第一个换行
getline(cin, ex);//接收魔板上面4个数
getline(cin, ey);//接收魔板下面4个数
magicboard endstate(ex, ey);//初始化一个目标状态
string sx = "1 2 3 4";
string sy = "8 7 6 5";
magicboard startstate(sx, sy);//初始化一个初始状态
queue<magicboard> ready;//存放搜索目标的队列
map<int,set<int> > pass;//存放已经到达过的状态的哈希表
pass[startstate.x].insert(startstate.y);//往哈希表中加入初始状态
ready.push(startstate);//把初始状态加入搜索队列
int flag = 0;//指示是否能到达的变量
//判断目标状态是不是就是初始状态,如果是,直接输出
if (startstate == endstate){
cout << startstate.stepValue() << endl;
continue;
}
//如果队列头的步数在限制范围内,那么进入循环
while (ready.front().stepValue() < n){
magicboard deal = ready.front();//获取队列头的魔板
ready.pop();//队列头的魔板出队
//进行操作A
magicboard dealA = deal;//操作A的魔板
dealA.opA();//进行操作A
//如果到达目标状态
if (dealA == endstate){
cout << dealA.stepValue() << " " << dealA.step << endl;
flag = 1;
break;
}
//如果进行操作A之后的状态没有见过,那么加入搜索队列中,并把这个状态放入哈希表中
if (pass[dealA.x].count(dealA.y)!=1){
ready.push(dealA);
pass[dealA.x].insert(dealA.y);
}
//进行操作B
magicboard dealB = deal;//操作B的魔板
dealB.opB();//进行操作B
//如果到达目标状态
if (dealB == endstate){
cout << dealB.stepValue() << " " << dealB.step << endl;
flag = 1;
break;
}
//如果进行操作B之后的状态没有见过,那么加入搜索队列中,并把这个状态放入哈希表中
if (pass[dealB.x].count(dealB.y) != 1){
ready.push(dealB);
pass[dealB.x].insert(dealB.y);
}
//进行操作C
magicboard dealC = deal;//操作C的魔板
dealC.opC();//进行操作C
//如果到达目标状态
if (dealC == endstate){
cout << dealC.stepValue() << " " << dealC.step << endl;
flag = 1;
break;
}
//如果进行操作B之后的状态没有见过,那么加入搜索队列中,并把这个状态放入哈希表中
if (pass[dealC.x].count(dealC.y) != 1){
ready.push(dealC);
pass[dealC.x].insert(dealC.y);
}
}
//如果无法到达,输出-1
if (flag == 0){
cout << "-1" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
} Soj-1515
和上面的一题一样,只是把操作和初始状态换了,换汤不换药的一题

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<map>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
struct magicboard{
int x;
int y;
string step;
magicboard(string xx, string yy){
x = (xx[0] - '0') * 1000 + (xx[2] - '0') * 100 + (xx[4] - '0') * 10 + (xx[6] - '0');
y = (yy[0] - '0') * 1000 + (yy[2] - '0') * 100 + (yy[4] - '0') * 10 + (yy[6] - '0');
step = "";
}
void opA(){
int x1 = x / 1000;
int x2 = x / 100 - x1 * 10;
int x3 = x / 10 - x1 * 100 - x2 * 10;
int x4 = x % 10;
int y1 = y / 1000;
int y2 = y / 100 - y1 * 10;
int y3 = y / 10 - y1 * 100 - y2 * 10;
int y4 = y % 10;
x = x3 * 1000 + x4 * 100 + x1 * 10 + x2;
y = y3 * 1000 + y4 * 100 + y1 * 10 + y2;
step += 'A';
}
void opB(){
int x1 = (x % 1000)*10;
int x2 = x / 1000;
x = x1 + x2;
int y1 = (y % 1000)*10;
int y2 = y / 1000;
y = y1 + y2;
step += 'B';
}
void opC(){
int x1 = x / 1000;
int x2 = x / 100 - x1*10;
int x3 = x / 10 - x1*100 - x2*10;
int x4 = x % 10;
int y1 = y / 1000;
int y2 = y / 100 - y1 * 10;
int y3 = y / 10 - y1 * 100 - y2 * 10;
int y4 = y % 10;
x = x1 * 1000 + x3 * 100 + y3 * 10 + x4;
y = y1 * 1000 + x2 * 100 + y2 * 10 + y4;
step += 'C';
}
int stepValue(){
return step.length();
}
bool operator==(magicboard e)const{
if (x == e.x&&y == e.y){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
};
int main(){
int n;
string ex;
string ey;
while (cin >> n, n != -1){
char c;
scanf("%c", &c);
getline(cin, ex);
getline(cin, ey);
magicboard endstate(ex, ey);
string sx = "1 2 3 4";
string sy = "5 6 7 8";
magicboard startstate(sx, sy);
queue<magicboard> ready;
map<int,set<int> > pass;
pass[startstate.x].insert(startstate.y);
ready.push(startstate);
int flag = 0;
if (startstate == endstate){
cout << startstate.stepValue() << endl;
continue;
}
while (ready.front().stepValue() < n){
magicboard deal = ready.front();
ready.pop();
//opA
magicboard dealA = deal;
dealA.opA();
if (dealA == endstate){
cout << dealA.stepValue() << " " << dealA.step << endl;
flag = 1;
break;
}
if (pass[dealA.x].count(dealA.y)!=1){
ready.push(dealA);
pass[dealA.x].insert(dealA.y);
}
//opB
magicboard dealB = deal;
dealB.opB();
if (dealB == endstate){
cout << dealB.stepValue() << " " << dealB.step << endl;
flag = 1;
break;
}
if (pass[dealB.x].count(dealB.y) != 1){
ready.push(dealB);
pass[dealB.x].insert(dealB.y);
}
//opC
magicboard dealC = deal;
dealC.opC();
if (dealC == endstate){
cout << dealC.stepValue() << " " << dealC.step << endl;
flag = 1;
break;
}
if (pass[dealC.x].count(dealC.y) != 1){
ready.push(dealC);
pass[dealC.x].insert(dealC.y);
}
}
if (flag == 0){
cout << "-1" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}Soj-1007
按规律把字符放一个2维矩阵再按顺序输出
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while (cin >> n, n != 0){
string x[201];//纵向的字符串
string s;
cin >> s;
int i = 0;
int count = 0;
while (i < s.length()){
if (count % 2 == 0){
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){
x[j] += s[i];
i++;
}
}
else{
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--){
x[j] += s[i];
i++;
}
}
count++;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){
cout << x[j];
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
} Soj-1036
 第一排字符,按从小到大是原字符表的纵列,先将其排序,再横向输出即可
第一排字符,按从小到大是原字符表的纵列,先将其排序,再横向输出即可
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
struct si{
int a;
char b;
si(int aa, int bb){
a = aa;
b = bb;
}
bool operator<(si aa)const{
if (b > aa.b){
return false;
}
else if(b < aa.b){
return true;
}
else{
if (a > aa.a){
return false;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
}
};
int main(){
string s;
while (cin >> s, s!="THEEND"){
string s2;
char p[1000][15];
multiset<si> m;
cin >> s2;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
si ss(i, s[i]);
m.insert(ss);
}
multiset<si>::iterator it = m.begin();
int k = 0;
for (; it != m.end(); it++){
for (int i = 0; i < (s2.length() / s.length()); i++){
p[i][(*it).a] = s2[k];
k++;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < (s2.length()/s.length()); j++){
for (int k = 0; k < s.length();k++){
cout << p[j][k];
}
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
} Soj-1006
 题目要求对于给定的几个预测结果,算出与所有预测距离最近的一个排列。
这题的关键是理解这个距离是怎么算的,举个例子:ABCDE和BCADE。对于ABCDE,排在A后面的是BCDE,排在B后面是CDE,而对于BCADE,排在A后面只有DE,排在B后面的还是有CDE,所以他们距离+2+0,按这样的规律算,可以算出总距离是2。
题目要求对于给定的几个预测结果,算出与所有预测距离最近的一个排列。
这题的关键是理解这个距离是怎么算的,举个例子:ABCDE和BCADE。对于ABCDE,排在A后面的是BCDE,排在B后面是CDE,而对于BCADE,排在A后面只有DE,排在B后面的还是有CDE,所以他们距离+2+0,按这样的规律算,可以算出总距离是2。
得到全排列
string c[120];
string t = "ABCDE";
c[0] = t;
for (int i = 1; next_permutation(t.begin(), t.end()); i++){
c[i] = t;
}#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
string c[120];
string t = "ABCDE";
c[0] = t;
for (int i = 1; next_permutation(t.begin(), t.end()); i++){
c[i] = t;
}
while (cin >> n,n!=0){
int d[120] = {};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
string a;
cin >> a;
for (int l = 0; l < 120; l++){
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++){
for (int k = j + 1; k < 5; k++){
if (a.find(c[l][j]) > a.find(c[l][k])){
d[l]++;
}
}
}
}
}
int best = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 120; i++){
if (d[i] < d[best]){
best = i;
}
}
cout << c[best] << " is the median ranking with value "<< d[best] << "." << endl;
}
return 0;
} Soj-1009
梅森素数
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int a[17] = { 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59 };
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
int i = 0;
while (a[i] < n){
i++;
long long int x = pow(2, a[i])-1;
long long int b = x;
int flag = 0;
for (long long int j = 2; j*j < x; j++){
if (x%j == 0){
x = x / j;
if (flag == 0){
cout << j;
flag = 1;
}
else{
cout << " * " << j;
}
}
}
if (flag == 1){
cout << " * " << x << " = " << b << " = " << "( 2 ^ " << a[i] << " ) - 1" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}Soj-1050
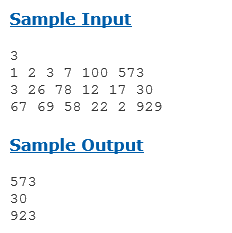
5个数字之间可以任意进行四则运算,求出不大于目标数的最大结果,使用深搜,需要注意的是,5个数字可以不全部用完,结果可以是负数。另外,除法必须要可以整除才能进行。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int target;
int flag;
int ans;
int add(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
int sub(int a, int b){
return a - b;
}
bool candivide(int a, int b){
if (b == 0) return false;
if (a%b == 0){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
int divide(int a, int b){
return a / b;
}
int multi(int a, int b){
return a*b;
}
void dfn(int a[], int b){
for (int i = 0; i < b; i++){
for (int j = i + 1; j < b; j++){
int x = a[i];
int y = a[j];
a[j] = a[b - 1];
//add
a[i] = add(x, y);
if (a[i] == target){
flag = 1;
return;
}
if (a[i]<target&&a[i]>ans){
ans = a[i];
}
dfn(a, b - 1);
//sub
a[i] = sub(x, y);
if (a[i] == target){
flag = 1;
return;
}
if (a[i]<target&&a[i]>ans){
ans = a[i];
}
dfn(a, b - 1);
//sub2
a[i] = sub(y, x);
if (a[i] == target){
flag = 1;
return;
}
if (a[i]<target&&a[i]>ans){
ans = a[i];
}
dfn(a, b - 1);
//multi
a[i] = multi(x, y);
if (a[i] == target){
flag = 1;
return;
}
if (a[i]<target&&a[i]>ans){
ans = a[i];
}
dfn(a, b - 1);
//divide
if (candivide(x, y)){
a[i] = divide(x, y);
if (a[i] == target){
flag = 1;
return;
}
if (a[i]<target&&a[i]>ans){
ans = a[i];
}
dfn(a, b - 1);
}
//divide2
if (candivide(y, x)){
a[i] = divide(y, x);
if (a[i] == target){
flag = 1;
return;
}
if (a[i]<target&&a[i]>ans){
ans = a[i];
}
dfn(a, b - 1);
}
//还原
a[i] = x;
a[j] = y;
}
}
}
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int num[5];
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++){
cin >> num[j];
}
cin >> target;
flag = 0;
ans = -99999999;
dfn(num, 5);
if (flag == 1){
cout << target<<endl;
}
else{
cout << ans<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}Soj-1443
输入的2个数字,第一个数字是总共有多少个数,第二个数字是我们所需的数所在的位置。第二行则是该列数字分别的优先度。在这一题里面,队列中的第一个数,如果是优先度最高的,就可以pop掉,否则放到队尾,最后输出的是我们所需的数字是第几个pop的。
使用一个队列queue放真正的位置,一个优先队列priority_queue存放优先度最高的

#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct q{
bool target;
int priority;
q(bool t, int p){
target = t;
priority = p;
}
bool operator<(q a)const{
if (priority < a.priority){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
};
int main(){
int t;
cin >> t;
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++){
int n,m;
queue<q>queue1;
priority_queue<q>queue2;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){
int p;
cin >> p;
if (j == m){
q ele(true, p);
queue1.push(ele);
queue2.push(ele);
}
else{
q ele(false, p);
queue1.push(ele);
queue2.push(ele);
}
}
int count = 0;
while (!queue1.empty()){
if (queue1.front().priority >= queue2.top().priority){
count++;
if (queue1.front().target){
break;
}
queue1.pop();
queue2.pop();
}
else{
queue1.push(queue1.front());
queue1.pop();
}
}
cout << count << endl;
}
return 0;
}Soj-1156
构建了一棵树,然后按先序遍历输出这棵树,这题需要注意的是我们在插入的同时要注意找出这棵树的根节点

#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct treenode{
treenode* left;
treenode* right;
char data;
int nodenum;
int leftnum;
int rightnum;
treenode(){
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
void preorder(treenode* t){
cout << (*t).data;
if ((*t).left != NULL){
preorder((*t).left);
}
if ((*t).right != NULL){
preorder((*t).right);
}
}
int main(){
int n;
while (scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){
treenode tree[2000];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int n, l, r;
char d;
cin >> n >> d >> l >> r;
tree[i].nodenum = n;
tree[i].leftnum = l;
tree[i].rightnum = r;
tree[i].data = d;
}
int flag[2000] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if (tree[i].leftnum == tree[j].nodenum){
tree[i].left = &(tree[j]);
flag[j] = 1;
}
if (tree[i].rightnum == tree[j].nodenum){
tree[i].right = &(tree[j]);
flag[j] = 1;
}
}
}
int x;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if (flag[i] == 0){
x = i;
break;
}
}
preorder(&(tree[x]));
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
} Soj-1024
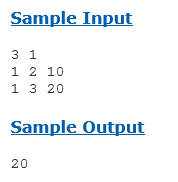
输入第一行的2个数字,第一个数字是总共有n个节点,第二个数字是起始点,第二行,是n-1行路径,然后求出国王最多能走多远,节点只能通过一次
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int s, e, d;
node(int ss, int ee, int dd){
s = ss;
e = ee;
d = dd;
}
};
int ans = 0;
map<int,vector<node> > ma;
int vis[20005] = {0};
void dfn(int k, int distance){
if (distance > ans){
ans = distance;
}
vis[k] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < ma[k].size(); i++){
if (vis[ma[k][i].e]!=1){
dfn(ma[k][i].e, distance + ma[k][i].d);
}
}
vis[k] = 0;
}
int main(){
int n, k;
while (scanf("%d %d",&n,&k) != EOF){
ans = 0;
int distance = 0;
ma.clear();
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){
int s, e, d;
cin >> s >> e >> d;
node edge(s, e, d);
node edge2(e, s, d);
ma[s].push_back(edge);
ma[e].push_back(edge2);
}
dfn(k, distance);
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}Soj-1063
根据输入的信息,查询对应id的员工的boss id和该员工所拥有的部下
相应的规则:
1
2
3
4
1.薪酬是唯一的
2.薪酬和身高都比你高的人是你的boss(薪酬>自己,身高>=自己)
3.你的部下必须是薪酬和身高都比你低的人
4.你部下的部下是你的部下(符合第三点)
这题使用的是先按薪酬排序,排完序之后,对于要查询的id,找到他的位置,从该位置开始往前扫描,遇到身高比他低的都是他的部下。要注意的是,当遇到一个身高比他高的人的时候,就可以停止继续扫描了,因为这个人薪酬比你低,身高比你高,他是你的同事,他前面身高薪酬比你低的都是他的部下,而同事的部下并不是你的部下。而找boss,则是从自己的位置往前扫,身高大于或者等于自己的那个人。

#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct person{
int id;
int salary;
int height;
void set(int i, int s, int h){
id = i;
salary = s;
height = h;
}
bool operator<(person p)const{
if (salary < p.salary){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
};
person p[30005];
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int m, q;
cin >> m >> q;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++){
int i, s, h;
cin >> i >> s >> h;
p[j].set(i, s, h);
}
sort(p, p + m);
int id;
for (int j = 0; j < q; j++){
cin >> id;
int count = 0;
int flag = 0;
int pos;
int boss = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++){
if (p[k].id == id){
pos = k;
for (int l = k + 1; l < m; l++){
if (p[l].height >= p[pos].height){
boss = p[l].id;
break;
}
}
break;
}
}
for (int k = pos - 1; k >= 0; k--){
if (p[k].height > p[pos].height){
break;
}
else{
count++;
}
}
cout << boss << ' ' << count << endl;
}
}
return 0;
} 1
Fin 10.27/20:30